There are significant differences between stainless steel heat exchange tubes and stainless steel fluid tubes in terms of usage, design requirements, structural characteristics, and application scenarios. The following is a specific analysis:
一、Purpose and core functions
1.Stainless steel heat exchange tube
Core function: Used for heat exchange equipment such as heat exchangers, condensers, evaporators, etc., to achieve heat transfer between two fluids through tube walls.
Key requirements: efficient heat transfer, anti scaling, and resistance to thermal stress. Stable operation is required in high temperature, high pressure, or corrosive environments, while optimizing surface area to improve heat transfer efficiency.
2.Stainless steel fluid pipe
Core function: Used for transporting various fluids (such as water, gas, oil, corrosive media, etc.), it is a key component of pipeline systems.
Key requirements: safe transportation, pressure resistance, corrosion resistance, low fluid resistance. It is necessary to ensure smooth fluid flow, avoid leakage, and adapt to pressure and medium erosion during long-term transportation.
二、Structural and design differences
1.Pipe structure
Heat exchange tube
Usually used as light tubes or special structural tubes (such as finned tubes, threaded tubes, corrugated tubes), heat transfer efficiency is improved by increasing the surface area (fins) or disturbing the fluid (threads/ripples).
The diameter of the pipe is usually small (usually with an outer diameter of 10-50mm), and the length is long (several meters to tens of meters), making it easy to arrange densely inside the heat exchanger.
The thickness of the pipe wall is relatively thin (to reduce thermal resistance), but it needs to balance pressure resistance and corrosion resistance. Thin walled seamless pipes or welded pipes may be used.
Fluid pipe
Mainly using light pipes, with smooth inner walls (reducing fluid resistance), uniform structure, and no additional heat transfer enhancement design.
The range of pipe diameters is wider (from a few millimeters to several hundred millimeters), selected according to the conveying flow rate and pressure; The wall thickness is designed according to the pressure level (such as low-pressure thin-walled pipes, high-pressure thick walled pipes).
2.Material selection
Both commonly use stainless steel (such as 304, 316L, 321, etc.), but with different emphasis:
Heat exchange tube: Pay more attention to the thermal conductivity of the material (such as 304 having better thermal conductivity than 316L) and its resistance to high temperature oxidation. Some scenarios require high-temperature resistant alloys (such as Inconel).
Fluid pipes: focus more on strength, toughness, and corrosion resistance, and need to adapt to the characteristics of the medium (such as 316L for chloride ion environments and 321 for high temperatures).
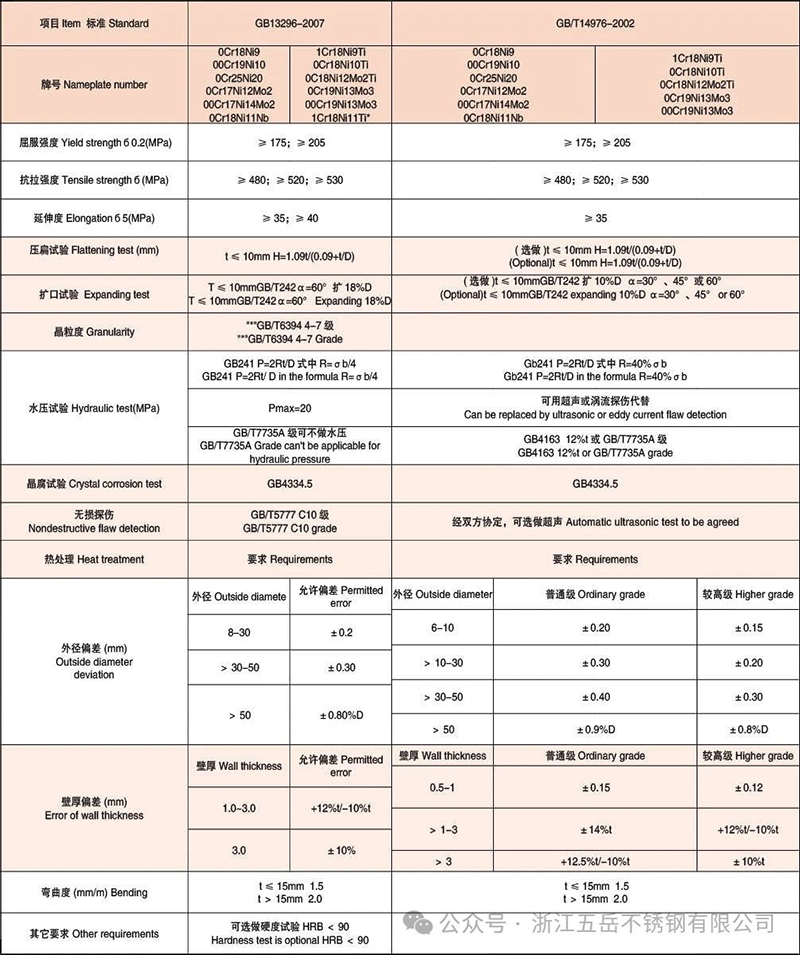
三、Manufacturing standards and inspection requirements
1.Manufacturer's standard
Heat exchange tube:Follow the specialized standards for heat exchangers, such as:
China: GB/T 14976 "Seamless Stainless Steel Tubes for Fluid Transport", GB/T 12771 "Welded Stainless Steel Tubes for Fluid Transport";
International: ASTM A312 (seamless and welded austenitic stainless steel pipes), EN 10216-5 (seamless steel pipes for high temperatures).
Fluid pipe:Follow fluid transport standards, such as:
China: GB/T 151 "Heat exchangers", GB/T 24593 "Seamless stainless steel pipes for boilers and heat exchangers";
International: ASME BPVC Section VIII (Pressure Vessels), ASTM A213 (Seamless Steel Tubes for Boilers and Superheaters).
2.Key inspection points
Heat exchange tube: It is necessary to test the heat transfer performance, tube sheet expansion/welding sealing, temperature difference stress resistance, and conduct water pressure test and eddy current testing (to detect internal defects).
Fluid pipes: focus on pressure testing (water pressure/air pressure), leakage detection, material mechanical properties (tensile/impact), and chemical composition analysis. Some require intergranular corrosion testing (for corrosive media).
四、Application scenarios
1.Typical applications of heat exchange tubes
Heat exchange equipment in the fields of petrochemicals (condenser, reboiler), electricity (steam generator), refrigeration (air conditioning evaporator), metallurgy (waste heat recovery), etc.
2.Typical Applications of Fluid Pipes
Chemical pipelines (transporting acidic and alkaline solutions), water supply and drainage systems, gas pipelines, food and pharmaceutical (sanitary grade pipelines), marine engineering for ships (seawater transportation), etc.
五、Summary and Comparison
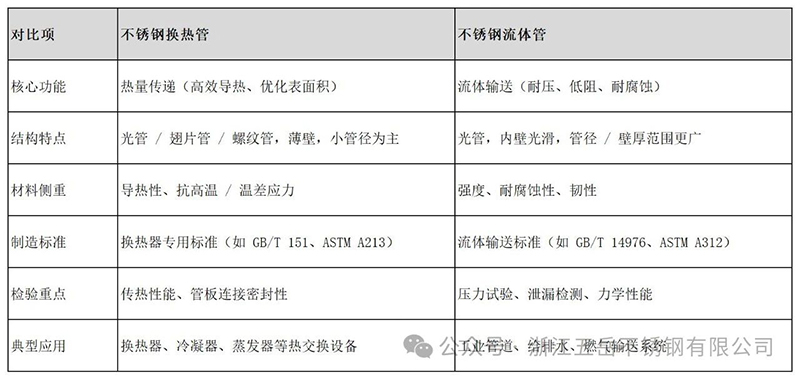
From the above differences, it can be seen that although both belong to stainless steel pipes, they have significant differences in design, manufacturing, and application due to their different functional orientations. It is necessary to choose the appropriate pipe material according to specific working conditions.

COPYRIGHT © 2025 Zhejiang Mingfeng Pipeline Equipment Co., Ltd
Enterprise information service provider:JCSW